Do business in Brazil
Want to onboard an employee in Latin America ?
Brazil is one of the largest and most dynamic economies in Latin America, offering significant opportunities for foreign investors and businesses looking to expand. With its vast market, diverse industries, and strategic location, Brazil continues to be a top destination for global enterprises. However, doing business in Brazil comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding the country’s legal, regulatory, and economic landscape is crucial for success.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know to do business in Brazil in 2024. From foreign investment regulations to corporate law, labor laws, and taxation, we’ll provide insights into key areas that impact your operations. Whether you’re entering the market for the first time or expanding an existing presence, this guide will help you navigate Brazil’s complex business environment with confidence.
Brazil at a Glance
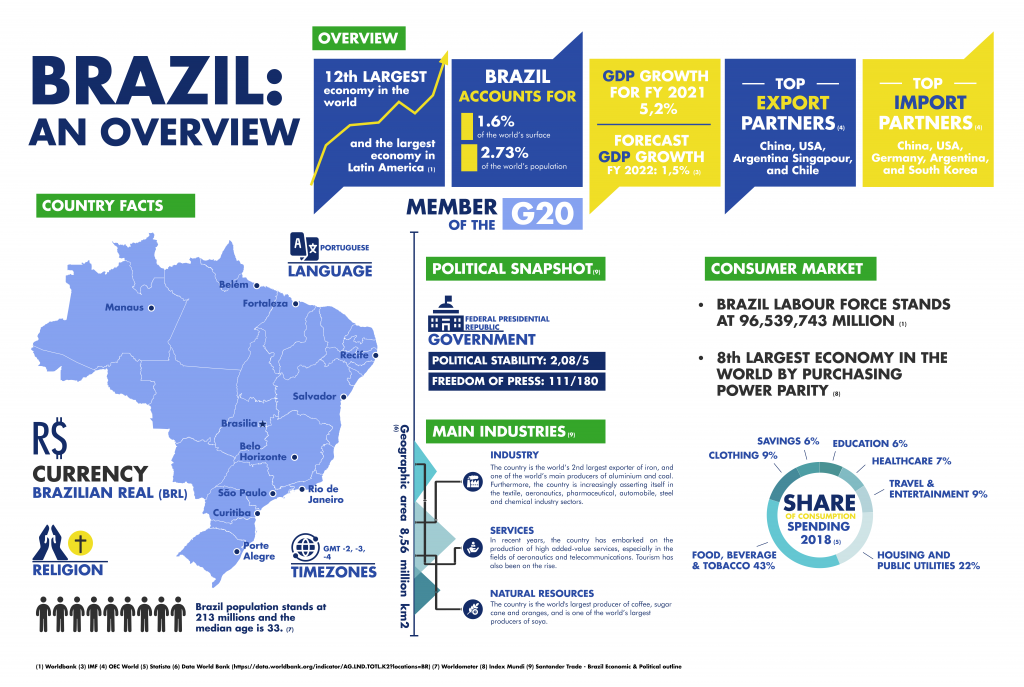
Overview of Brazil's Economic Landscape
Brazil boasts the largest economy in Latin America and ranks as one of the world’s top emerging markets. Its diverse economy spans various sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, energy, and technology. The country is a global leader in the production of commodities like soybeans, coffee, and iron ore. Additionally, Brazil’s renewable energy sector, particularly hydroelectric power, plays a crucial role in its energy matrix.
The Brazilian market offers immense potential for businesses looking to expand. With a population of over 210 million, there is a large consumer base and a growing middle class that fuels demand for goods and services. Moreover, the government continues to attract foreign investment by modernizing infrastructure and offering incentives for key industries.
However, to successfully do business in Brazil, companies must navigate economic fluctuations, a complex tax system, and regulatory challenges. Understanding Brazil’s economic landscape and staying informed about market trends is essential for long-term success in this vibrant market.
Key Industries and Market Opportunities
Brazil is home to a wide range of thriving industries, each offering significant market opportunities for businesses looking to do business in Brazil. The agriculture sector remains a cornerstone of Brazil’s economy, with the country being a global leader in the production of soybeans, sugar, coffee, and beef. These exports not only drive economic growth but also offer opportunities for investment in agribusiness technology and logistics.
The energy sector is another area of rapid expansion, especially in renewable energy. Brazil is one of the top producers of hydroelectric power and has been making strides in solar and wind energy. This makes it an attractive market for companies involved in green technology and sustainable solutions.
In addition, technology and innovation are gaining momentum, particularly in cities like São Paulo and Curitiba, which have become tech hubs for startups. Brazil’s growing middle class has also spurred the rise of e-commerce, fintech, and digital services, creating demand for innovation in financial technology, logistics, and retail.
Agriculture & Agribusiness
Energy & Renewable
Tech & Innovation
Foreign Investment in Brazil
Regulations and Incentives for Foreign Investors
Brazil has developed a robust framework of regulations and incentives to attract foreign investors and encourage economic growth. The government offers several incentives, including tax breaks, financial support, and special regimes for specific sectors like technology, manufacturing, and infrastructure. For example, the « Inovar-Auto » program promotes innovation in the automotive industry, while the Special Regime for the Export and Import of Goods Used in Oil and Gas Exploration (REPETRO) benefits companies in the energy sector.
Additionally, BACEN (the Central Bank of Brazil) plays a key role in regulating foreign investments and ensuring transparency in capital inflows and outflows. Investors are required to register foreign capital with BACEN, which monitors financial transactions and ensures compliance with currency exchange regulations. This process safeguards Brazil’s financial system while facilitating foreign direct investment.
Despite these incentives, foreign investors must navigate complex regulations. Brazil’s investment laws allow foreign companies to hold 100% ownership in most industries, but certain sectors—such as healthcare and media—still have restrictions. Furthermore, Brazil has strict labor laws and a complex tax system, which requires careful planning and compliance. For businesses looking to do business in Brazil, working with local experts and legal professionals can help ensure compliance and make the most of available incentives.
How to Set Up and Expand Your Business
To successfully set up a business in Brazil, foreign investors must follow a series of legal and administrative steps. The process begins with choosing the right legal structure, such as a limited liability company (LTDA) or a corporation (S.A.), based on the business’s needs. Investors must then register the company with the Brazilian Board of Trade, obtain a taxpayer number (CNPJ), and register for social security and labor taxes. It’s essential to adhere to local labor laws, which include mandatory benefits and employee protections.
Expanding your business in Brazil requires strategic planning and market analysis. Foreign companies often benefit from forming partnerships with local firms, which can help navigate cultural nuances and regional market conditions. Additionally, Brazil’s large internal market offers substantial growth opportunities, but companies must adapt to the country’s diverse regions. Understanding regional economic dynamics and consumer behavior is key for successful expansion in Brazil’s vast and varied market.
For expert guidance on setting up or expanding your business in Brazil, reach out to Europartner to get started today.
Immigration and Work Visas
When planning to do business in Brazil and hire foreign employees, understanding visa requirements and navigating immigration laws is crucial. Brazil offers several types of work visas, including temporary and permanent visas, depending on the nature of the employment. For example, the VITEM V (temporary work visa) is commonly used for foreign professionals coming to Brazil for employment purposes, and it can be extended based on the length of the contract. Companies must sponsor foreign workers and provide detailed documentation, such as proof of employment, contracts, and tax compliance, to ensure the visa application is successful.
Navigating Brazil’s immigration laws can be complex, as they require compliance with both federal and local regulations. Additionally, employers must register foreign employees with the Ministry of Justice and the Brazilian Federal Police upon their arrival in the country. Staying updated on visa categories, such as those for investors, executives, or highly skilled professionals, is essential to avoid delays and legal issues. Partnering with experienced professionals who understand the intricacies of Brazil’s immigration system can help streamline the hiring process and ensure compliance with local laws. For more details on the different work visa options and how to get them, visit our article on Work Visa in Brazil.
Corporate Law
When you plan to do business in Brazil, choosing the right legal structure is essential for success. Brazil offers several types of business entities, with the most common being the Limited Liability Company (LTDA) and the Corporation (S.A.). The LTDA is often preferred by small to medium-sized businesses due to its flexible structure, fewer regulatory requirements, and the fact that owners’ liability is limited to their capital contribution. On the other hand, larger companies or those planning to raise capital in the stock market typically choose the S.A. structure, which offers more formal governance but also requires more stringent compliance.
Before forming a business in Brazil, it’s important to consider key factors such as capital requirements, tax obligations, and local regulations. Understanding labor laws, including the hiring process and employee benefits, is crucial to avoid legal issues. Companies must also register with the Brazilian Board of Trade and obtain a CNPJ (Brazilian Taxpayer ID) to operate legally. It’s advisable to work with legal and accounting professionals to ensure full compliance with local laws and to choose the structure that best suits your business goals. By selecting the appropriate legal structure and following the correct steps, businesses can establish a solid foundation for growth and success in Brazil.
Taxation in Brazil
Overview of Brazil’s Tax System & Corporate Taxes
Brazil has one of the most complex tax systems in the world, and businesses looking to do business in Brazil must understand its intricacies to stay compliant. The tax structure includes federal, state, and municipal taxes, each with specific rules and rates. Key taxes for businesses include Corporate Income Tax (IRPJ), Social Contribution on Net Profit (CSLL), and Value-Added Tax (ICMS), among others. The IRPJ is calculated at a rate of 15%, with an additional 10% surcharge on profits exceeding a certain threshold, while CSLL is levied at a rate of 9%.
Key Considerations for Business Formation
Compliance with corporate taxes in Brazil requires meticulous record-keeping and timely tax filings. Companies must adhere to strict reporting requirements, including monthly or quarterly tax declarations, depending on their size and structure. Furthermore, businesses are subject to complex payroll taxes and contributions, such as INSS (social security), FGTS (severance fund), and PIS/COFINS (social integration contributions). Failing to comply with these requirements can lead to heavy penalties. To manage this complexity, many companies seek professional advice to ensure full tax compliance and efficient business operations.
By understanding Brazil’s tax system and meeting corporate tax compliance requirements, businesses can avoid legal issues and focus on growth in this dynamic market.
Labor Law and Employment Regulations
When you do business in Brazil, understanding the country’s labor laws and employment regulations is essential. Brazil’s labor laws, governed by the Consolidation of Labor Laws (CLT), ensure that employees receive a wide range of rights, including overtime pay, annual leave, and mandatory benefits like the 13th-month salary. Compliance is key, as failure to adhere to these regulations can result in heavy penalties for employers. Brazil also has strict rules regarding employee dismissal, severance pay, and working hours. Foreign companies must ensure they follow all local labor regulations when hiring, onboarding, and managing employees. For businesses looking to operate in Brazil, partnering with local experts can simplify compliance and reduce risk.
For a more in-depth understanding of Brazil’s employment regulations, visit our Brazil Employment Law – Full Guide.
Navigating the Brazilian Business Landscape with Europortage
Brazil offers vast opportunities for businesses ready to tap into its growing economy, diverse industries, and large consumer base. However, its complex legal, tax, and labor systems require careful navigation. From understanding corporate structures to complying with strict labor laws and navigating regional tax codes, expanding into Brazil requires thorough preparation. By partnering with local experts, like Europortage, businesses can simplify the process, ensure compliance, and focus on building a successful presence in the Brazilian market. With the right support, your business can thrive in this promising and dynamic economy.
Ready to take the next step? Contact us today and learn how Europortage can help you do business in Brazil with confidence.


















































