In the first quarter of every year, every Brazilian citizen must declare income tax. However, they declare it only if their annual income exceeds a specific amount. The Brazilian individual income tax known as “Leão” has existed since 1922.
In this article we will explain what income tax is, who must file an annual tax statement, and when to file it. In addition, we’ll take a look at what you must declared and what are companies’ obligations.
See the topics we will cover below:
Table of Contents
Income tax in Brazil
The Income Tax is an annual tax levied on the individuals and companies’ incomes by the Federal Government. The government requires workers and businesses to report their annual income to the Receita Federal.
In that statement, the taxpayer needs to report all service income and expenses for the previous year.
The period is usually from the beginning of March to the end of April. As the income individual tax is a tax levied on citizens and companies, it exists two categories: Individual Income Tax (IRPF) and Corporate Income Tax (IRPJ).
The Individual Income Tax (IRPF)
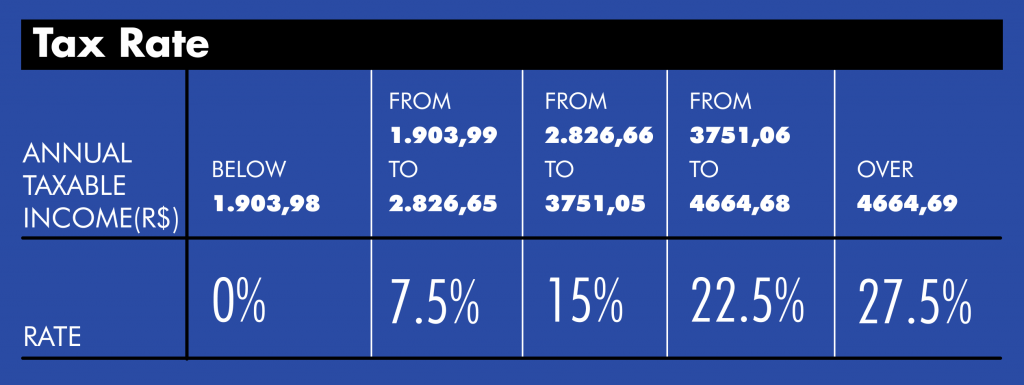
The IRPF is progressive according to the employee’s salary.
Find below the tax rates :
You need help to fill your statement ? Check our step-by-step guide !
The Corporate Income Tax (IRPJ) - For PJ contracts
The IRPJ is a tax levied on all companies with an active CNPJ in Brazil. Contractors with a PJ contract are part of this category. The government calculates the tax based on the profit yearly earned. In general, the IRPJ is levied on any company that operates and generates revenue in Brazil.
Who must file an individual tax statement ?
Basically, if you fall into any of the categories below, you must file your income tax return in 2022:
- Income: Individuals who has earned taxable income above the threshold (R $28,559.70) in the past year. If you have earned tax-exempt income above the threshold (R $40,000) in the past year. For example, it could be labor indemnities, savings accounts or donations.
- Ownership of property: If you own property with a total value above R $ 300,000.
- Stock market transactions: If you have carried out operations on stock and commodities.
- Rural activity: If you have earned annual gross revenue from rural activity above R$142,798.50.
- Capital Gain: If you are exempted from the tax on your property sale’s capital gains according to the article 39 of Law no. 11.196 / 2005.
- Resident in Brazil: If you became a resident in Brazil during the past year.
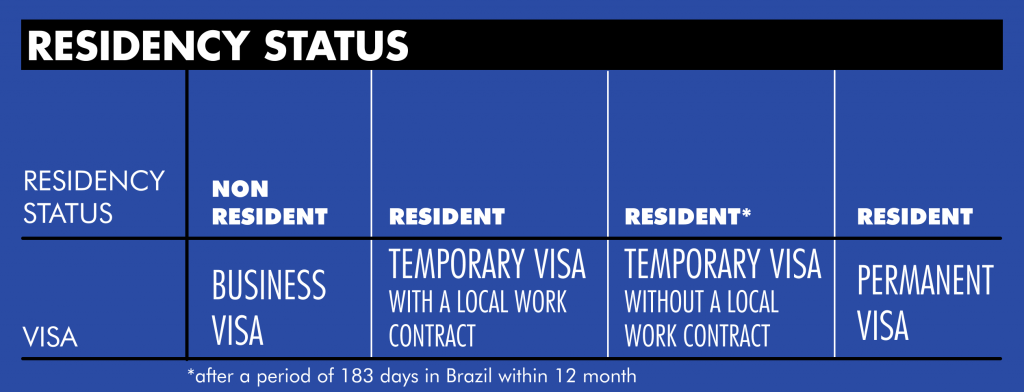
Residents VS Non-residents
The individual income taxation in Brazil depends on the individual’s tax residence status. Indeed, the Brazilian government differenciates the resident and the non-resident.
As well, the government differentiate the residents from the non-residents. Firstly, resident individuals are taxed on their worldwide income. Secondly, non-residents are taxed only on income from Brazilian sources.
Those who fail to render accounts to the government will have to pay a fine in the minimum amount of R$ 165.74. Further, this amount can rise up to 20% of the total tax due. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the rules and deadlines.
What must be declared in the statement?
It is pivotal to present an income declaration from all sources. Indeed, taxpayers should report all information they receive as employees, contractors under the RPA contract, business partners or retirees. As well, individuals have to include foreign sources in the declaration mentioned above. Also, they must declare incomes received from other people, such as rents and non taxable income such as savings accounts.
Deductions and Exemptions
The deductions and exemptions includes the following four items:
- Dependants: A specific amount per dependant is established each year.
- Alimony payments in Brazil or overseas.
- Tuition expenses, in Brazil or abroad, limited to a fixedamount.
- Medical charges, in Brazil or abroad, are deductible (when not reimbursed).
- Brazilian social security contributions made by the individual.
- Private pension contributions limited to 12% of gross taxable income.
As well, other deductions could be done as:
- Donation made to the government and its entities
- Contribution to cultural projects.
All taxpayers could have the benefit of the following annual deduction: 20% of gross taxable income, limited to R$ 16,754.34)
Taxpayers who receive income from their work (RPA contract) can deduct the following items:
- Expenses made to third parties
- Payments to produce the business’ revenue.
- Investments and expenses to maintain the business.
What are companie’s duties regarding the employees’ individual income tax?
The main obligation of all companies that paid withholding income tax (IRRF) is the responsibility to generate and publish income reports.
The company must submit the income statement. The income statement is a document employees must have to fill the individual income tax statement. The government will fine companies that are behind the deadline for submitting documents. They will also fine them for submitting incorrect information.
The employer also needs to send the Declaração de Imposto de Renda Retido na Fonte (DIRF) to the Receita Federal. The document contains the amounts paid to employees and withholdings for donations, such as PIS and Cofins.
When should the statement be submitted?
The income report must be delivered by the company to the employee on the last working day of February of the year. For example, for the 2022 fiscal year, the income report for the 2021 calendar year must be delivered, and so on.
In this report, there must be a financial income report notifying the nature and value of the service, deductions, and withholding tax, according to the total annual value.
2022 UPDATES: Shorter deadline – this year the deadline starts on 07 March and runs until 29 April.
Is it necessary to send it to all employees?
Every company legally established in Brazil that pays employees, suppliers, or other legal entities must send a revenue report to all, even if the employee does not fall into the mandatory reporting category. This is a right that assists those who work and need to fulfill the taxpayer’s obligations.
Also, partners of companies with a monthly income of more than 1,903.98 reais or a total value of more than 28,559.70 reais are also entitled to this document. Even individual microentrepreneurs (MEI) must send their income reports to their employees.
How can Europortage benefits your business ?
We are an Employer of Record (EOR) company in Brazil. With our EOR and Payroll Services, we hire and onboard your candidates while managing compliance. Besides, we manage your payroll in Brazil. Do you have a project in Brazil ? Contact us now!


















































